| Version 4 (modified by , 14 years ago) (diff) |
|---|
TITAN- Tiny Task Networks - Cookbook
This document includes instructions how to install and to run TITAN.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Titan is a framework for the distributed execution of context recognition algorithms within Body Area Network (BANs). The framework‘s central component is running on a mobile phone or a PC. It organizes and controls the execution of task plans which are distributed on the mobile phone, body worn devices, and smart objects in the environment of its user. A task plan describes what resources (sensors, processing units, and actuators) are needed to achive a specific context/activity recognition goal.
The Titan framework integrates SENSEI’s resource-oriented approach to distributed processing within the sensor islands themselves. Similar to the Execution Manager (EM), Titan is coordinating the execution of a plan, monitors the executed session and adapts distributed processing to local changes in the network topology by reconfiguring sensor nodes within subseconds. Extending the concepts of the Execution Manager to the sensor islands enables to execute and monitor a plan more locally. The support of local task operation enforces the stability of the execution in case of failure or disconnection (Locality).
Architectural Overview
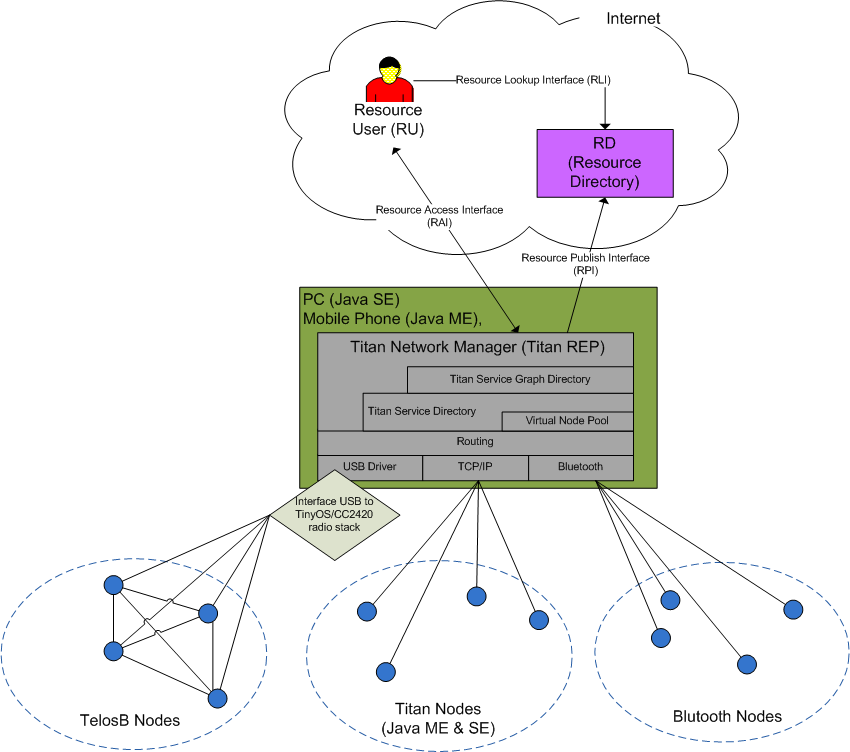
The Figure below shows the Integration of the Titan framework in the SENSEI system. The framework’s central component is both implemented in Java SE and Java ME (Personal Profile). It runs on every device supporting one of these two Java platforms. It has been tested on a Windows XP/Vista/7 Machine and on a HTC Touch HD running a Windows Mobile 6.1 OS and IBM J9 Java Virtual Machine. The Titan framework supports by now the following types of nodes: wireless sensor nodes running on TinyOS with the CC2420 radio stack (we used TelosB nodes), any device supporting Java ME Personal Profile (Java Titan Node), and Bluetooth nodes with a custom protocol.
Every sensor node in the Titan framework provides certain resources (e.g. sensor, actuator, or processing resource). Titan is periodically scanning the network and registering the resources of the available nodes in the Titan Resource Directory. All context/activity recognition tasks are defined by a task plan (also called resource graph) in the Titan Task Plan Database. Titan can start such a recognition task, by mapping the task plan to the available resources found in the Titan Resource Directory.
The Titan framework is integrated as a Java REP to the SENSEI system. It registers to the SENSEI system as a Resource through the Resource Publish Interface (RPI). A Resource User (RU) can access Titan through the Resource Access Interface (RAI). Depending on the executed task plan, the Resource User receives data from the Titan Framework.
Installation
Hardware and Software Requirements
Installing the TITAN requires the following hardware tools and software packages:
- A Computer running an OS supporting Java SE
- Optional: Mobile device supporting Java ME Personal Profile
- Optional: One or more TelosB Nodes and TinyOS-2.1.1
Installing TITAN Network Manager
On a PC
On a Mobile Device supporting Java SE PersonalProfile?
Installing the Nodes
TelosB Sensor Nodes
At least two TelosB nodes are needed. One of the sensor nodes will be connected via USB to the machine running the TITAN Network Manager and will act as the communication interface for the Titan Network Manager (TITAN Communication Node). The other nodes are used as service provider for the Titan Framework. Every node gets an ID which is defined during compilation time. ID 0 is reserved for the TITAN Communication Node.
The software implementing Titan in TinyOS-2.1. for the TelosB sensor platform is located in the TITAN/TELOSB directory. Please change to this directory.
In the file TitanInternal?.h you can define the communication channel in which the network is working:
#define TITAN_COMM_CHANNEL CC2420_DEF_CHANNEL
Compile the code with the following command:
make telosb
Now plug-in one of the nodes to the USB port. With the TinyOS command motelist you should be able to see the connected sensor node:
Reference CommPort Description ---------- ---------- ---------------------------------------- M4A6J3WH /dev/ttyUSB0 tmote sky
We want now to install TITAN on the TelosB platform with the ID 0, to create the TITAN Communication Node.
make telosb reinstall.<ID> bsl,/dev/<COMPORT>
where <ID> is in this case 0, and <COMPORT> the CommPort? of the pluged-in device (use motelist).
Repeate the last step to install TITAN on the other nodes. Increase the ID number for every additional node (IDs must be unique!). To run the Titan Network Manager with TelosB support:
- Connect the Titan Communication Node to the machine, on which the TITAN Network Manager should run.
- Edit following parameters in the code of the class ch.ethz.ee.ife.sensei.titanmanager.rep.REPServerMain:
TitanConnector.m_tmote=true; TitanConnector.m_tmote_comport=<COMPORT>;
Test the TITAN Framewok
To test the framework you can use the ResourceUser?-Client GUI located in the TitanDesktop? Eclipse-Project: ch.ethz.ee.ife.sensei.titanresourceuser.TitanResourceUserMain?. Start the TitanREP on a PC or mobile device as described above and run the RU-Client GUI.
- Browse the TitanREP: Use the RU-Client to browse the TitanREP. All avaiable service graphs (acting as SENSEI Resources) can be shown.
- Edit service graphs: A RU can edit/add/delete service graphs from the TitanREP.
- Start/Stop? a service graph: A service graph can be started and stopped by a RU. RU's can subscribe to a running service graph to be notified of the results. Currently TITAN supports no parallel execution of service graphs.
You can test the execution with the examples given in the path TITAN_Desktop\RUClient\xml\ServiceGraph_descriptions
Attachments (2)
- titan_arch.PNG (63.1 KB) - added by 14 years ago.
- titan_arch.png (62.9 KB) - added by 14 years ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip