| Version 8 (modified by , 14 years ago) (diff) |
|---|
EMR – Energy-efficient Multi-hop Routing for Clustered WS&ANs Cookbook
This document aims to introduce about how to use the resource of Energy-efficient Multi-hop Routing (EMR). It first gives some background about EMR about its main objective and how it operates. Then the required devices and soft wear environment to install EMR are provided. After illustrate how to install the codes, it briefly explains how to run this routing solution.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Hot-spot issue means the phenomenon that some nodes in a WSN drain energy more rapidly than others, due to the higher load, and thus deplete energy earlier. Therefore hot-spot issue may differ node lifetime in the network. The main purpose of EMR is to address the hot-spot issue in WSNs via individual node lifetime equalization across the network, so that the network energy could be better utilized. The operation of EMR is summarized as following:
- First of all, some CH candidates are selected;
- Then, these candidates compete to be the final CH;
- After the CHs are selected, they announce their role and allow non-CH nodes to join them as member nodes to form the clusters;
- Then each CH gives a slot to each member node belongs it and collects the data packets from its respective member nodes;
- Finally, each CH aggregates these packets as one summary packet of its cluster and delivers them to the sink.
Please note that the competition ranges of the CH candidates to be the CHs are determined by the probability of the nodes to be the CH, acquired by the mathematical analysis about how the node lifetime could be equalized across the network.
Installation
Hardware and Software Requirements
Installing the EMR protocol requires the following hardware tools and software packages:
- Linux PC (Ubuntu)/ Windows XP
- JAVE Environment jdk-6u21
- TinyOS-2.x
- EMR software package
- At least 11 TelosB sensor nodes (one as sink, and others as normal nodes consisting a network)
We assume that the installation PC is running a Linux operating system, and the TinyOS-2.x and JAVA environment have been installed and configured properly. We skip the installation of TinyOS. A user could refer to TinyOS-2.x about the installation if necessary. Please note that the description about how to install the EMR routing solution is based on the Ubuntu operating system.
In a WSN, there are two types of nodes, the normal sensor nodes which form the network, and the sink. The data packets from the normal nodes are periodically collected by the sink after some basic processing at the CH, e.g. data aggregation. The following provides the detailed information about the structure and the content of the EMR software package:
- Node
EMRAPPc.nc
Contains the configuration files and the wiring between interfacesEMRCHC.nc
Contains all relevant actions and behavior of the Cluster Head (CH), e.g. collecting the informaiton of the member nodes like how many member nodes belong it, receiving the data packets from the member nodes, and forwarding the summary packet of the cluster towards the sinkEMRClusteringC.nc
Contains the procedure about how the clusters are formedEMRInitC.nc
Contains all initializations of each round across the network operation, and how to process the received messageEMRLib.nc
Contains general functionalities that could be used by other modules, e.g. the energy consumption modelEMRMemberC.nc
Contains all recelvant actions and behavior of the member nodes, e.g. to determine which CH it belongs to, and to send data to the CHEMRRouting.nc
Contains the process about how to determine the routing towards the sink in multi-hop scenario- Interface
Contains the defination of all involved interfaces - include
Contains all header files
- Sink
EMRSinkAppc.nc
Contains the configuration files and the wiring between interfacesEMRSinkC.nc
Contains the actions and behavior of the sinkEMRSink.h
Header file
Installation
- First of all, a user needs to install and configure TinyOS-2.x and JAVE Environment jdk-6u21 properly
- Then the user could copy the
buildfolder and theMakefileinto a new folder under the tinyOS directory for normal node
/opt/tinyOS2.x/emr/node/
- Thirdly, copy the source code into a new folder for sink node
/opt/tinyOS2.x/emr/sink/
- Now, the user can load the binary code into normal nodes by
# make telosb reinstall.<node ID> bsl,/dev/ttyUSB*
- And finally compile and load the binary code into sink nodes by
# make telosb install.100 bsl,/dev/ttyUSB*
Running EMR
The following describes about how to run EMR step by step and how to test whether it is installed properly.
- Operation
- First, turn on all normal nodes. After a normal node is powered on, its red led will on, meaning that this node is waiting for clustering indication from the sink node.
- Then, turn on the Sink node.
- When the sink node is on, the network starts operation, e.g. the CHs are selected, the clusters are organized and the data packets from the member nodes are collected by the CHs
- During the operation, you should be able to see that different leds are on on the nodes from time to time, where a bue led means a CH, a green led means a member node and a red led means that this node has depleted its energy and died. Please note that each change of the node led means a novel round.
- Monitor the debug messages
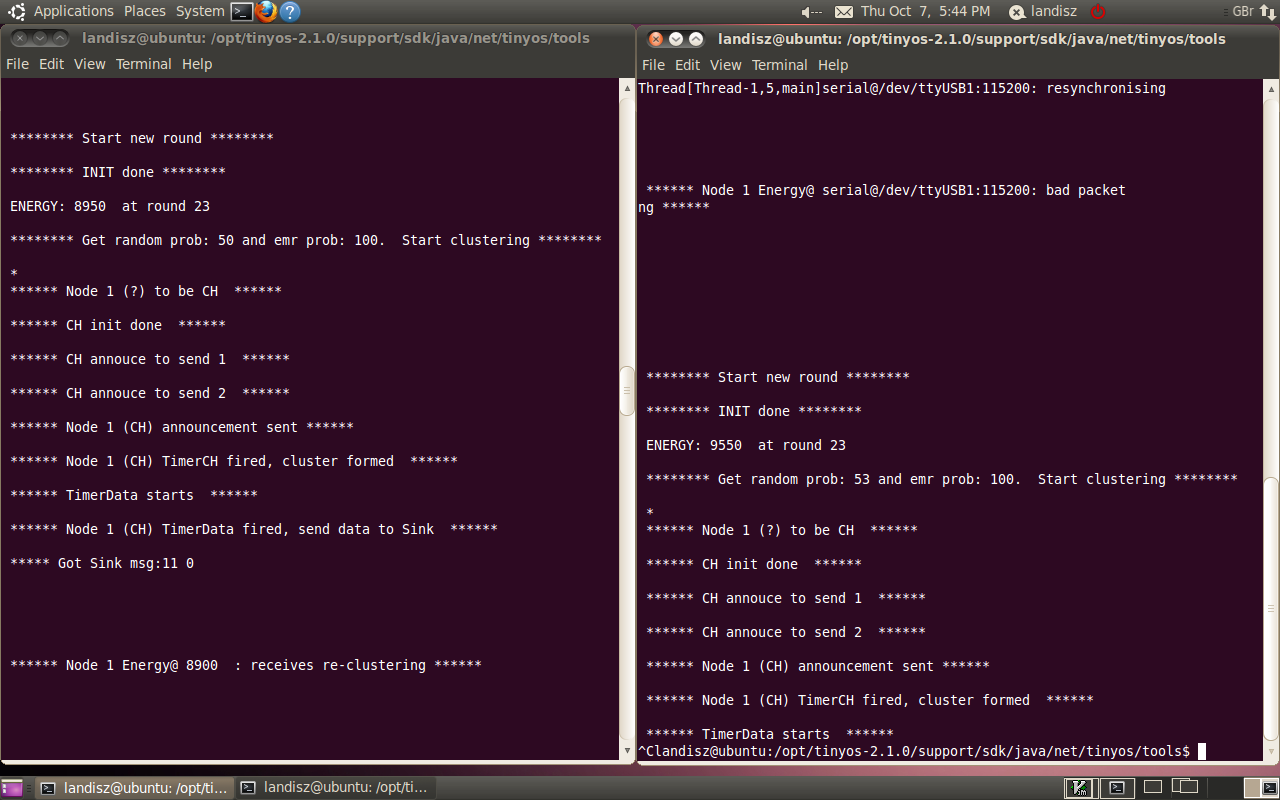
A user is able to use the serial output to watch the debug messages:
# java net.tinyos.tools.PrintfClient -comm serial@/dev/ttyUSB*:telosb
The debug messages should start to be shown in the terminal as below:
- Change parameters
A user is able to change the parameters, e.g.
control_packet_size,data_packet_sizefreely in the funcitonsend_parameter()in the fileEMRSinkC.nc
Attachments (3)
-
debug_msg.png (127.8 KB) - added by 14 years ago.
debug_msg.png
- Node status.jpg (97.3 KB) - added by 14 years ago.
- GUI-demo.jpg (153.1 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip